Introduction:
Microfinance has emerged as a critical tool in driving financial inclusion, especially in developing economies like India. Over the years, the integration of financial technology (Fintech) has brought about a paradigm shift in the microfinance sector, enhancing accessibility, efficiency, and sustainability.
With the Global Microfinance market projected to grow by USD 122.46 billion from 2021 to 2026 at a CAGR of 11.61%, Fintech’s role in this growth is undeniable. The increasing demand for financial inclusion and the rise of digital platforms are key drivers of this growth trend
The Current State of Microfinance – India
As of March 31, 2024, the sector’s gross loan portfolio (GLP) stood at an astounding INR 4.33 lakh crore—a 24.5% increase from the previous year. This ecosystem supports nearly 7.8 crore unique borrowers through 14.9 crore loan accounts, highlighting its critical role in empowering individuals and communities.
Interestingly, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) have taken the lead in this space, holding a significant 39.1% market share, while banks account for 33.5%. This shift underscores how alternative financial institutions are stepping up to meet the diverse needs of borrowers.
With the help of Fintech solutions, MSMEs now have access to tailored loan products that cater to their unique requirements. A Statista report revealed that average loan sizes for medium-sized enterprises reached over INR 9 million in Q4 FY23, showcasing how technology is enabling these businesses to thrive.
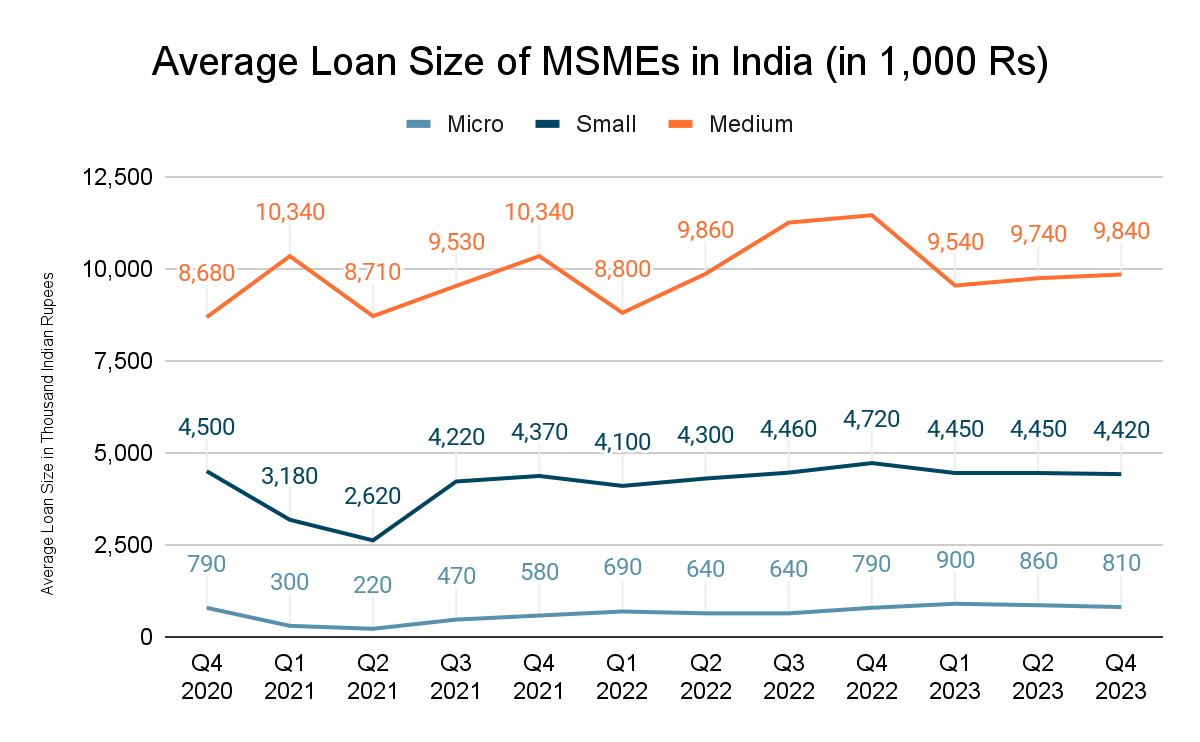

The Role of Fintech in Microfinance:
1. Enhancing Financial Inclusion:
Fintech platforms have expanded the reach of microfinance to underserved populations by leveraging digital technologies such as mobile banking, digital wallets, and online lending platforms. These innovations have enabled:
- Faster Loan Approvals: Digital processes significantly reduce turnaround times for loan disbursement.
- Accessibility: Mobile-based platforms make financial services available in remote areas, eliminating the need for physical bank branches.
2. Improving Operational Efficiency:
Fintech has streamlined microfinance operations by introducing automated workflows, reducing overhead costs, and enhancing transparency. Key contributions include:
- Digital Lending Platforms: Automation of loan application and approval processes.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Use of AI and data analytics for better portfolio management and risk assessment.
3. Addressing Credit Risk with Data Analytics:
Traditional microfinance models often relied on limited credit data, posing challenges in risk assessment. Fintech solutions now employ:
- AI-Powered Credit Scoring: Algorithms analyze alternative data sources, such as transaction history and mobile usage patterns, to evaluate creditworthiness.
- Predictive Analytics: Anticipating defaults and managing risk effectively.
4. Facilitating Financial Literacy:
Fintech apps often incorporate financial literacy modules to educate borrowers about financial management, repayment strategies, and savings, fostering responsible borrowing behavior
5. Enabling Scalability and Profitability:
With Fintech, Microfinance institutions (MFIs) can scale their operations efficiently. The integration of digital tools has:
- Increased yields by reducing credit costs.
- Supported profitability despite challenges, as seen in the rising profitability of Indian MFIs post-pandemic.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Challenges
- Data Privacy Concerns: With the increasing reliance on digital platforms, ensuring data security and privacy is critical.
- Adoption Barriers: Lack of digital literacy among borrowers can hinder adoption.
Opportunities
- Collaboration with NBFCs: Fintech’s collaboration with NBFCs offers opportunities for innovative loan products.
- Expansion into New Markets: Leveraging AI and blockchain can facilitate growth in untapped markets.
Conclusion:
The integration of fintech in microfinance has redefined how financial services are delivered, making them more inclusive, efficient, and scalable. As technology continues to evolve, its role in addressing existing challenges and unlocking new opportunities in the microfinance sector will only grow, paving the way for a more financially inclusive world.

