Characteristics of Good Quality Seeds
1. Genetic Purity
This is the seed’s true-to-type nature. In other words, the plant, tree, or seedling that grows from the seed must resemble its mother completely. In order to increase the crop’s yield, resistance, or other quality features, it is imperative to have this quality trait.
2. Physical Quality
It is the separation of pure seeds from contaminated or inert material. The seed’s dimensions, weight, colour, and texture ought to be all the same. Also, it must be devoid of inert objects such as stones, dust, dirt, leaves, twigs, stalks, and flowers. It shouldn’t have seeds that are shrivelled, infected, spotted, stained, or damaged.
The seed should be simple to identify as belonging to a particular species. The value of seed planting and field establishment may be indirectly impacted by this quality character. Through adequate cleaning and grading (processing) of the seed after collecting, this quality can be obtained with seed lots.
3. Physiological Quality
This is how the seed actually manifests and grows. Seed germination and seed vigour are examples of the physiological quality traits of seeds. The ability of a seed to survive is measured by its viability.
The ability of a seed to develop a healthy seedling or a seed with typical root and shoot growth under optimum conditions is known as germination. The ability of a seed to create superior seedlings is referred to as seed vigour.
The ability of a seed to regenerate in any situation is the result of all of its characteristics. The level of performance of the seed and lot during germination, seedling emergence, and in the future is determined by the seed vigour.
4. Seed Health
Absence of fungal or insect infestations indicates how healthy the seed is. The physiological quality and physical quality of seeds that have been infested by insects or fungi will decline over time when they are stored. Another sign of a healthy seed is low vigour.
Their health is directly impacted by the seed quality character, which is warranted for soundness in seed to generate superior seedlings in the field or nursery.
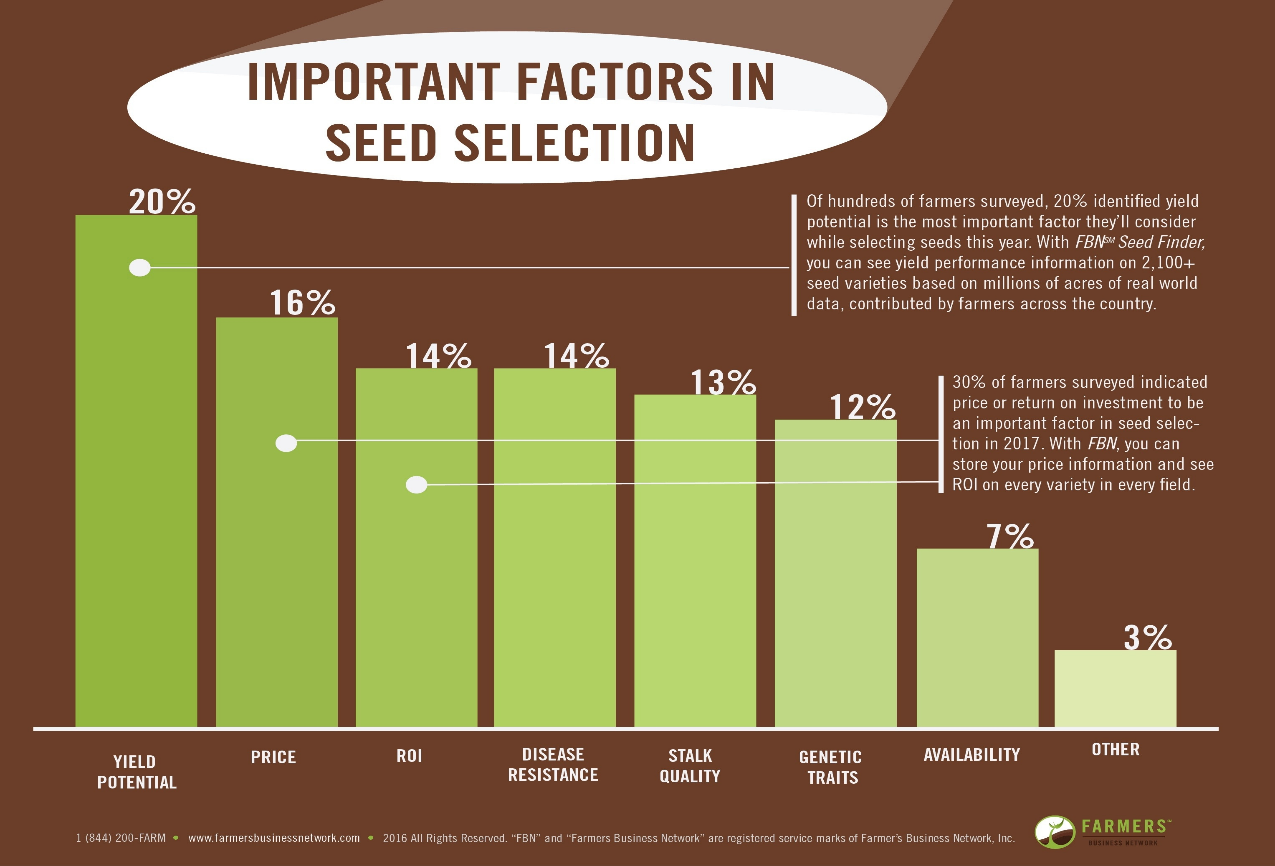

Method of Seed Selection
Seed selection is the most important factor of yield. The choice of seeds is a crucial part of cultivation; good seeds should always be used so that we may get greater crop production. Seed selection is also one of the best strategies to increase a farmer’s yield.
The basis of a robust, high quality crop is laid by the input known as seed. The quality of the seed is essential for good crop output.
It is important to remember that while planting any crop, the quality of the seed must not be compromised. It is crucial that the seeds are only planted after being treated. This can shield crops from ailments brought on by various seeds.
Before planting the seed in the field, the germination rate should be assessed. Take a cotton cloth, piece of paper, or jute bag for this, moisten it, and keep a count of some seeds on it. Only seed it after determining the percentage of its deposition a few days later.
Germination % = No. of germinated seeds/total seeds kept for germination × 100
Why Is Seed Treatment Necessary?
Seed treatment before sowing is done for the following reasons.
- To break the dormancy of the seed
- For early seed germination and disease prevention

